All of hippke's Comments + Replies
What about the Landauer limit? We are 3 orders of magnitude from the Landauer limit ( J/op), see my article here on Lesswrong. The authors list several physical limitations, but this one seems to be missing. It may pose the most relevant limit.
That's an excellent question, pondered by the brightest minds. The great Freeman Dyson proposed a solution dubbed eternal intelligence (Dyson 1979, Reviews of Modern Physics, Volume 51, Issue 3, July 1979, pp.447-460). Basically, some finite amount of matter=energy is stored. As the universe cools over time, energy costs per computation decrease (logarithmically, but forever). After each cooling time period, one can use some fraction of the remaining energy, which will thus never go to zero, leading to eternal consciousness.
It was later understood th...
I think this calculation is invalid. A human is created from a seed worth 700 MB of information, encoded in the form of DNA. This was created in millions of years of evolution, compressing/worth a large (but finite) amount of information (energy). A relevant fraction of hardware and software is encoded in this information. Additional learning is done during 20 years worth 3 MWh. The fractional value of this learning part is unknown.
Sure! I argue that we just don't know whether such a thing as "much more intelligent than humans" can exist. Millions of years of monkey evolution have increased human IQ to the 50-200 range. Perhaps that can go 1000x, perhaps it would level of at 210. The AGI concept makes the assumption that it can go to a big number, which might be wrong.
From what I understand about "ELO inflation", it refers to the effect that the Top 100 FIDE players had 2600 ELO in 1970, but 2700 ELO today. It has been argued that simply the level increased, as more very good players entered the field. The ELO number as such should be fair in both eras (after playing infinitely many games...). I don't think that it is an issue for computer chess comparisons. Let me know if you have other data/information!
I ran the experiment "Rebel 6 vs. Stockfish 13" on Amazon's AWS EC2. I rented a Xeon Platinum 8124M which benched at 18x 1.5 MNodes/s. I launched 18 concurrent single-threaded game sets with 128 MB of RAM for each engine. Again, ponder was of, no books, no tables. Time settings were 40 moves in 60s + 0.6 per move, corresponding to 17.5 MNodes/move. For reference, SF13 benches at ELO 3630 at this setting (entry "64 bit"); Rebel 6.0 got 2415 on a Pentium 90 (SSDF Computer Rating List (01-DEC-1996).txt, 90 kN/move).
The result:
- 1911 games played
- 18 d
- With a baseline of 10 MNodes/move for SF3, I need to set SF13 to 0.375 MNodes/move for equality. That's a factor of 30. Caveat: I only ran 10 games which turned out equal, and only at 10 MNodes/move for SF3.
- Yes: Rebel6 at normal 2021 settings (40 moves in 15 min) can be approximately matched with SF13 at 20 kNodes/move. More precisely: I get parity between Rebel6 (128 MB) and SF13 (128 MB) for 16 MNodes/move vs. 20 kNodes/move (=factor of 800x). On my Intel Core-M 5Y31 (750 kNodes/s), that's 21s vs. 0.026s per move. Note that the figure shows SF8, not SF13.
- I was contacted by one person via PM, we are discussing the execution setup. Otherwise, I could do it by the end of July after my vacation.
I ran the experiment "Rebel 6 vs. Stockfish 13" on Amazon's AWS EC2. I rented a Xeon Platinum 8124M which benched at 18x 1.5 MNodes/s. I launched 18 concurrent single-threaded game sets with 128 MB of RAM for each engine. Again, ponder was of, no books, no tables. Time settings were 40 moves in 60s + 0.6 per move, corresponding to 17.5 MNodes/move. For reference, SF13 benches at ELO 3630 at this setting (entry "64 bit"); Rebel 6.0 got 2415 on a Pentium 90 (SSDF Computer Rating List (01-DEC-1996).txt, 90 kN/move).
The result:
- 1911 games played
- 18 d
OK, I have added the Houdini data from this experiment to the plot:
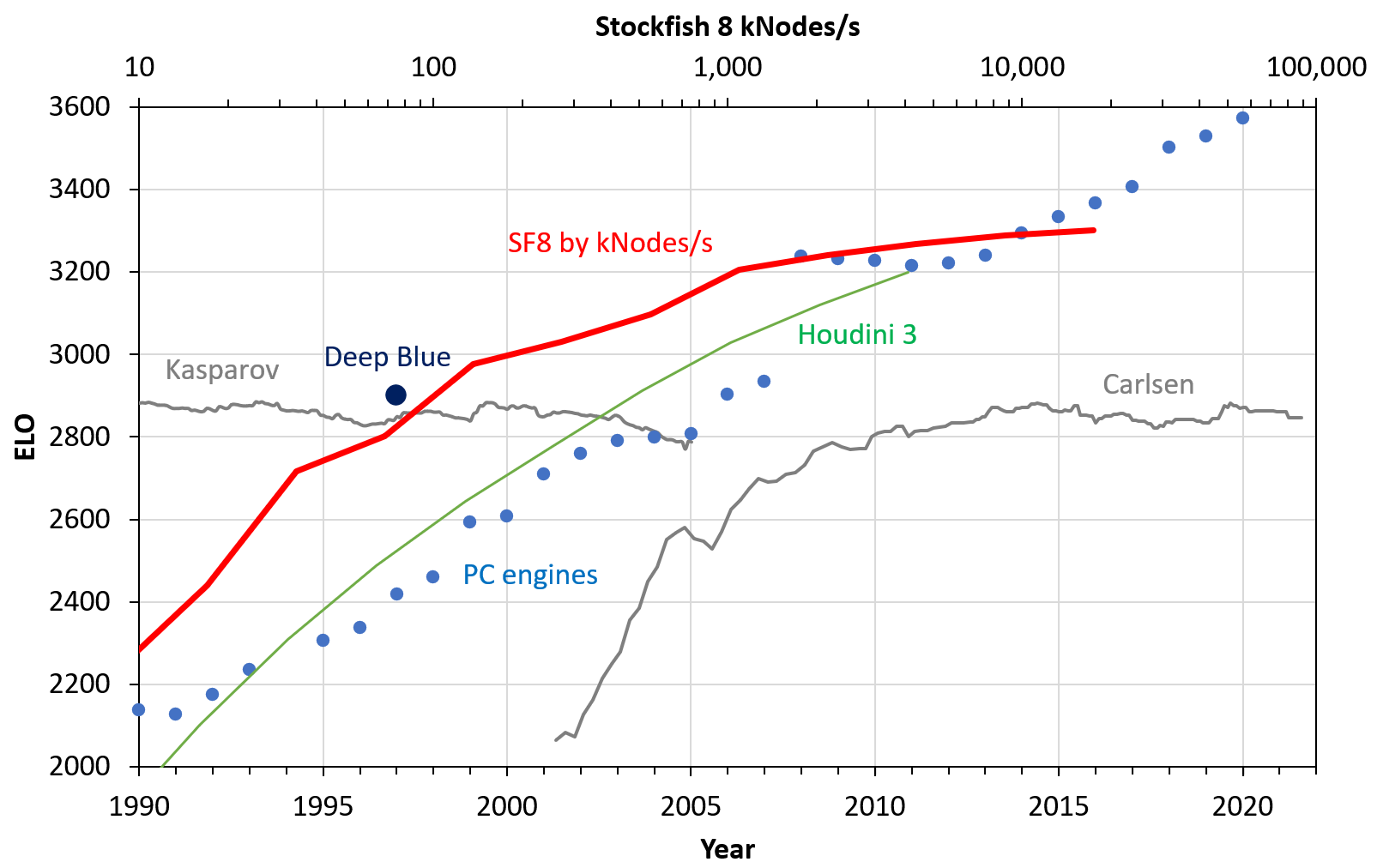
The baseline ELO is not stated, but likely close to 3200:
| Experiment | kNodes/move | ELO drop | ELO calculated |
| 4k nodes vs 2k nodes | 2 | 303 | 1280 |
| 8k nodes vs 4k nodes | 4 | 280 | 1583 |
| 16k nodes vs 8k nodes | 8 | 237 | 1863 |
| 32k nodes vs 16k nodes | 16 | 208 | 2100 |
| 64k nodes vs 32k nodes | 32 | 179 | 2308 |
| 128k nodes vs 64k nodes | 64 | 156 | 2487 |
| 256k nodes vs 128k nodes | 128 | 136 | 2643 |
| 512k nodes vs 256k nodes | 256 | 134 | 2779 |
| 1024k nodes vs 512k nodes | 512 | 115 | 2913 |
| 2048k nodes vs 1024k nodes | 1024 | 93 | 3028 |
| 4096k nodes vs 2048k nodes | 2048 | 79 | 3121 |
| Baseline | 4096 | 3200 |
Mhm, good point. I must admit that the "70 ELO per doubling" etc. is forum wisdom that is perhaps not the last word. A similar scaling experiment was done with Houdini 3 (2013) which dropped below 70 ELO per doubling when exceeding 4 MNodes/move. In my experiment, the drop is already around 1 MNode/move. So there is certainly an engine dependence.
From what I understand about the computer chess community:
- Engines are optimized to win in the competitions, for reputation. There are competitions for many time controls, but most well respected are the CCC with games of 3 to 15 minutes, and TCEC which goes up to 90 minutes. So there is an incentive to tune the engines well into the many-MNodes/move regime.
- On the other hand, most testing during engine development is done at blitz or even bullet level (30s for the whole game for Stockfish). You can't just play thousands of long games after each code commit
Yes, that's correct. It is slightly off because I manually set the year 2022 to match 100,000 kNodes/s. That could be adjusted by one year. To get an engine which begins its journey right in the year 2021, we could perform a similar experiment with SF14. The curve would be virtually identical, just shifted to the right and up.
Good point: SF12+ profit from NNs indirectly.
Regarding the ELO gain with compute: That's a function of diminishing returns. At very small compute, you gain +300 ELO; after ~10 doublings that reduces to +30 ELO. In between is the region with ~70 ELO; that's where engines usually operate on present hardware with minutes of think time. I currently run a set of benchmarks to plot a nice graph of this.
i) To pick a reference year, it seems reasonable to take the mid/late 1990s:
- Almost all chess engines before ~1996 lacked (or had serious inefficiencies) using multi-cores (very lengthy discussion here).
- Chess protocols became available, so that the engine and the GUI separated. That makes it straightforward to automate games for benchmarking.
- Modern engines should work on machines of that age, considering RAM constraints.
- The most famous human-computer games took place in 1997: Kasparov-Deep Blue. That's almost a quarter of a century ago (nice round n...
The MIPS are only a "lookup table" from the year, based on a CPU list. It's for the reader's convenience to show the year (linear), plus a rough measure of compute (exponential).
The nodes/s measure has the problem that it is engine-dependent.
The real math was done by scaling down one engine (SF8) by time-per-move, and then calibrating the time to the computers of that era (e.g., a Quad i7 from 2009 has 200x the nodes/s compared to a PII-300 from 1999)
Yes, that is a correct interpretation. The SF8 numbers are:
MIPS = [139814.4, 69907, 17476, 8738, 4369, 2184, 1092, 546.2, 273.1, 136.5, 68.3, 34.1, 17.1, 8.5, 4.3]
ELO = [3407,3375,3318,3290,3260,3225,3181,3125,3051,2955,2831,2671,2470,2219,1910]
Note that the range of values is larger than the plotted range in the Figure. The Figure cuts off at a 80486DX 33 MHz, 27 MIPS, introduced May 7, 1990.
To derive an analytical result, it is reasonable to interpolate with a spline and then subtract. Let me know if you have a specific question (e.g. for the year 2000).
As you can see in my Figure in this post (https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/75dnjiD8kv2khe9eQ/measuring-hardware-overhang), Leela (Neural Network based chess engine) has a very similar log-linear ELO-FLOPs scaling as traditional algorithms. At least in this case, Neutral Networks scale slightly better for more compute, and worse for less compute. It would be interesting to determine if the bad scaling to old machines is a universal feature of NNs. Perhaps it is: NNs require a certain amount of memory, etc., which gives stronger constraints. The conclusion would be that the hardware overhang is reduced: Older hardware is less suitable for NNs.
Thank you for your interest: It's good to see people asking similar questions! Also thank-you for incentivizing research with rewards. Yes, I think closing the gaps will be straightforward. I still have the raw data, scripts, etc. to pick it up.
i) old engines on new hardware - can be done; needs definition of which engines/hardware
ii) raw data + reproduction - perhaps everything can be scripted and put on GitHub
iii) controls for memory + endgame tables - can be done, needs definition of requirements
iv) Perhaps the community can already agree on a set of experiments before they are performed, e.g. memory? I mean, I can look up "typical" values of past years, but I'm open for other values.
At the Landauer kT limit, you need kWh to perform your FLOPs. That's 10,000x the yearly US electricity production. You'd need a quantum computer or a Dyson sphere to solve that problem.
Right. My experiment used 1 GB for Stockfish, which would also work on a 486 machine (although at the time, it was almost unheard of...)
(a) The most recent data points are from CCRL. They use an i7-4770k and the listed tournament conditions. With this setup, SF11 has about 3500 ELOs. That's what I used as the baseline to calibrate my own machine (an i7-7700k).
(b) I used the SF8 default which is 1 GB.
(c) Yes. However, the hardware details (RAM, memory bandwidth) are not all that important. You can use these SF9 benchmarks on various CPUs. For example, the AMD Ryzen 1800 is listed with 304,510 MIPS and gets 14,377,000 nodes/sec on Stockfish (i.e., 19.9 nodes per MIPS). The oldest CPU in the ...
I think the biggest improvement in this report can be made regarding Appendix D. The authors describe that they use "process size rather than transistor size" which is, as they correctly note, a made-up number. What should be used instead is transistor density (transistors per area), which is readily available in much detail for many past nodes, and the most recent "5nm" nodes (see e.g., wikichip).