I read the book years ago "to find out what all the fuss was about" and I was surprised to find that the book was only about white America for the most part.
After thinking about it, my opinion was that Murray should have left out the one chapter about race (because that discussion consumed all the oxygen and also) because the thing I was very surprised by, and which seemed like a big deal, and which potentially was something that could be changed via policy, and thus probably deserved most of the oxygen, was the story where:
the invisible migration of the twentieth century has done much more than let the most intellectually able succeed more easily. It has also segregated them and socialized them.
The story I remember from the book was that colleges entrance processes had become a sieve that retained high IQ whites while letting low IQ whites pass through and fall away.
Then there are low-IQ societies where an underclass lives with nearly no opportunity to see role models doing similar things in substantially more clever ways.
My memory is that the book focused quite a bit on how this is not how college used to work in the 1930s or so, and that it was at least partly consciously set up...
(3) tax businesses for hogging up all the smart people, if they try to brain drain into their own firm?
Due to tax incidence, that's the same as taxing smart people for getting together. I don't like that for two reasons. First, people should be free to get together. Second, the freedom of smart people to get together could be responsible for large economic gains, so we should be careful about messing with it.
What's with the neglect of Richard J. Herrnstein?! His name actually comes first on the cover!
I mostly agree with this review, but it endorses some rather poor parts of the book.
Properly administered IQ tests are not demonstrably biased against social, economic, ethnic, or racial groups. ... Charles Murray doesn’t bother proving the above points. These facts are well established among scientists.
Cultural neutrality is not well established. The Bell Curve's claims here ought to be rephrased as something more like "the cultural biases of IQ tests are equivalent to the biases that 20th century academia promoted". I've written about this here and here.
the gap between the adopted children with two black parents and the adopted children with two white parents was seventeen points, in line with the B/W difference customarily observed. Whatever the environmental impact may have been, it cannot have been large.
This seems to assume that parental impact constitutes most of environmental impact. Books such as The Nurture Assumption and WEIRDest People have convinced me that this assumption is way off. The Bell Curve has a section on malparenting seemed plausible to me at the time it was written, but which now looks pretty misguided (in much the same way as mainstream social science was/is misguided).
Just for context, I'd like to point out that the SAT has been revised and renormed since 1994 (twice IIRC). Current test scores are not straightforwardly comparable to the scores discussed in the book and in the post.
Imagine a world where having [a post mentioning the bell curve] visible on the frontpage runs a risk of destroying a lot of value. This could be through any number of mechanisms like
- The site is discussed somewhere, someone claims that it's a home for racism and points to this post as evidence. [Someone who in another universe would have become a valueable contributor to LW] sees this (but doesn't read the post) it and decides not to check LW out.
- A woke and EA-aligned person gets wind of it and henceforth thinks all x-risk related causes are unworthy of
In my capacity as moderator, I saw this post this morning and decided to leave it posted (albeit as Personal blog with reduced visibility).
I think limiting the scope of what can be discussed is costly for our ability to think about the world and figure out what's true (a project that is overall essential to AGI outcomes, I believe) and therefore I want to minimize such limitations. That said, there are conversations that wouldn't be worth having on LessWrong, topics that I expect would attract attention just not worth it–those I would block. However, this post didn't feel like where I wanted to draw the line. Blocking this post feels like it would be cutting out too much for the sake of safety and giving the fear of adversaries too much control over of us and our inquiries. I liked how this post gave me a great summary of controversial material so that I now know what the backlash was in response to. I can imagine other posts where I feel differently (in fact, there was a recent post I told an author it might be better to leave off the site, though they missed my message and posted anyway, which ended up being fine).
It's not easy to articulate where I think the line is or why...
Elsewhere you write (and also ask to consolidate, so I'm responding here):
The main disagreement seems to come down to how much we would give up when disallowing posts like this. My gears model still says 'almost nothing' since all it would take is to extend the norm "let's not talk about politics" to "let's not talk about politics and extremely sensitive social-justice adjacent issues", and I feel like that would extend the set of interesting taboo topics by something like 10%.
I think I used to endorse a model like this much more than I do now. A particular thing that I found sort of radicalizing was the "sexual preference" moment, in which a phrase that I had personally used and wouldn't have associated with malice was overnight retconned to be a sign of bigotry, as far as I can tell primarily to score points during the nomination hearings for Amy Coney Barrett. (I don't know anything special about Barrett's legal decisions or whether or not she's a bigot; I also think that sexual orientation isn't a choice for basically anyone at the moment; I also don't think 'preference' implies that it was a choice, any more than my 'flavor preferences' are my choice instead of being an uncont...
This is a helpful addendum. I didn't want to bust out the slippery slope argument because I didn't have clarity on the gears-level mechanism. But in this case, we seem to have a ratchet in which X is deemed newly offensive, and a lot of attention is focused on just this particular word or phrase X. Because "it's just this one word," resisting the offensive-ization is made to seem petty - wouldn't it be such a small thing to give up, in exchange for inflicting a whole lot less suffering on others?
Next week it'll be some other X though, and the only way this ends is if you can re-establish some sort of Schelling Fence of free discourse and resist any further calls to expand censorship, even if they're small and have good reasons to back them up.
I think that to someone who disagrees with me, they might say that what's in fact happening is an increase in knowledge and an improvement in culture, reflected in language. In the same way that I expect to routinely update my picture of the world when I read the newspaper, why shouldn't I expect to routinely update my language to reflect evolving cultural understandings of how to treat other people well?
My response to this objection would be ...
My observation tells me that our culture is currently in need of marginally more risky spaces, even if the number of safe spaces remains the same.
Our culture is desperately in need of spaces that are correct about the most important technical issues, and insisting that the few such spaces that exist have to also become politically risky spaces jeopardizes their ability to function for no good reason given that the internet lets you build as many separate spaces as you want elsewhere.
I’m going to be a little nitpicky here. LW is not “becoming,” but rather already is a politically risky space, and has been for a long time. There are several good reasons, which I and others have discussed elsewhere here. They may not be persuasive to you, and that’s OK, but they do exist as reasons. Finally, the internet may let you build a separate forum elsewhere and try to attract participants, but that is a non-trivial ask.
My position is that accepting intellectual risk is part and parcel of creating an intellectual environment capable of maintaining the epistemic rigor that we both think is necessary.
It is you, and others here, who are advocating a change of the status quo to create a bigger wall between x-risk topics and political controversy. I think that this would harm the goal of preventing x-risk, on current margins, as I’ve argued elsewhere here. We both have our reasons, and I’ve written down the sort of evidence that would cause me to change my point of view.
Fortunately, I enjoy the privilege of being the winner by default in this contest, since the site’s current norms already accord with my beliefs and preferences. So I don’t feel the need to gather evidence to pe...
Our culture is desperately in need of spaces that are correct about the most important technical issues
I also care a lot about this; I think there are three important things to track.
First is that people might have reputations to protect or purity to maintain, and so want to be careful about what they associate with. (This is one of the reasons behind the separate Alignment Forum URL; users who wouldn't want to post something to Less Wrong can post someplace classier.)
Second is that people might not be willing to pay costs to follow taboos. The more a space is politically safe, the less people like Robin Hanson will want to be there, because many of their ideas are easier to think of if you're not spending any of your attention on political safety.
Third is that the core topics you care about might, at some point, become political. (Certainly AI alignment was 'political' for many years before it became mainstream, and will become political again as soon as it stops becoming mainstream, or if it becomes partisan.)
The first is one of the reasons why LW isn't a free speech absolutist site, even tho with a fixed population of posters that would probably help us be more correct. But the second and third are why LW isn't a zero-risk space either.
It would be really nice to be able to stand up to left wing political entryism, and the only principled way to do this is to be very conscientious about standing up to right wing political entryism, where in this case “right wing” means any politics sufficiently offensive to the left wing, regardless of whether it thinks of itself as right wing.
"Stand up to X by not doing anything X would be offended by" is obviously an unworkable strategy, it's taking a negotiating stance that is maximally yielding in the ultimatum game, so should expect to receive as little surplus utility as possible in negotiation.
(Not doing anything X would be offended by is generally a strategy for working with X, not standing up to X; it could work if interests are aligned enough that it isn't necessary to demand much in negotiation. But given your concern about "entryism" that doesn't seem like the situation you think you're in.)
If someone proposes to do A by doing B, and B by doing C, they are proposing doing A by doing C. (Here A = "stand up to left wing entryism", B = "stand up to right wing entryism", C = "don't do things that left wing people are offended by")
EDIT: Also, the situation isn't symmetrical, since Steven is defining right-wing to mean things the left wing is offended by, and not vice versa. Hence it's clearly a strategy for submitting to the left, as it lets the left construct the left/right dichotomy.
The implied game is:
Step 1: The left decides what is offensively right-wing
Step 2: LW people decide what to say given this
Steven is proposing a policy for step 2 that doesn't do anything that the left has decided is offensively right-wing. This gives the left the ability to prevent arbitrary speech.
If the left is offended by negotiating for more than $1 in the ultimatum game, Steven's proposed policy would avoid doing that, thereby yielding. (The money here is metaphorical, representing benefits LW people could get by talking about things without being attacked by the left)
The relevant actors aren't consciously being strategic about it, but I think their emotions are sensitive to whether the threat of being offended seems to be working. That's what the emotions are for, evolutionarily speaking. People are innately very good at this! When I babysit a friend's unruly 6-year-old child who doesn't want to put on her shoes, or talk to my mother who wishes I would call more often, or introspect on my own rage at the abject cowardice of so-called "rationalists", the functionality of emotions as a negotiating tactic is very clear to me, even if I don't have the same kind of deliberative control over my feelings as my speech (and the child and my mother don't even think of themselves as doing game theory at all).
(This in itself doesn't automatically negate your concerns, of course, but I think it's an important modeling consideration: animals like Godzilla may be less incentivizable than Homo economicus, but they're more like Homo economicus than a tornado or an avalanche.)
due to the mechanisms described in "Entangled Truths, Contagious Lies" and "Dark Side Epistemology"
I'm not advocating lying. I'm advocating locally preferring to avoid subjects that force people to either lie or alienate people into preferring lies, or both. In the possible world where The Bell Curve is mostly true, not talking about it on LessWrong will not create a trail of false claims that have to be rationalized. It will create a trail of no claims. LessWrongers might fill their opinion vacuum with false claims from elsewhere, or with true claims, but either way, this is no different from what they already do about lots of subjects, and does not compromise anyone's epistemic integrity.
I'm not advocating lying.
I understand that. I cited a Sequences post that has the word "lies" in the title, but I'm claiming that the mechanism described in the cited posts—that distortions on one topic can spread to both adjacent topics, and to people's understanding of what reasoning looks like—can apply more generally to distortions that aren't direct lies.
Omitting information can be a distortion when the information would otherwise be relevant. In "A Rational Argument", Yudkowsky gives the example of an election campaign manager publishing survey responses from their candidate, but omitting one question which would make their candidate look bad, which Yudkowsky describes as "cross[ing] the line between rationality and rationalization" (!). This is a very high standard—but what made the Sequences so valuable, is that they taught people the counterintuitive idea that this standard exists. I think there's a lot of value in aspiring to hold one's public reasoning to that standard.
Not infinite value, of course! If I knew for a fact that Godzilla will destroy the world if I cite a book that I would otherwise would have cited as genuinely relevant, then fine, for the sake of the sa...
Your posts seem to be about what happens if you filter out considerations that don't go your way. Obviously, yes, that way you can get distortion without saying anything false. But the proposal here is to avoid certain topics and be fully honest about which topics are being avoided. This doesn't create even a single bit of distortion. A blank canvas is not a distorted map. People can get their maps elsewhere, as they already do on many subjects, and as they will keep having to do regardless, simply because some filtering is inevitable beneath the eye of Sauron. (Distortions caused by misestimation of filtering are going to exist whether the filter has 40% strength or 30% strength. The way to minimize them is to focus on estimating correctly. A 100% strength filter is actually relatively easy to correctly estimate. And having the appearance of a forthright debate creates perverse incentives for people to distort their beliefs so they can have something inoffensive to be forthright about.)
The people going after Steve Hsu almost entirely don't care whether LW hosts Bell Curve reviews. If adjusting allowable topic space gets us 1 util and causes 2 utils of damage distributed evenly acr...
I agree that offense-takers are calibrated against Society-in-general, not particular targets.
As a less-political problem with similar structure, consider ransomware attacks. If an attacker encrypts your business's files and will sell you the encryption key for 10 Bitcoins, do you pay (in order to get your files back, as common sense and causal decision theory agree), or do you not-pay (as a galaxy-brained updateless-decision-theory play to timelessly make writing ransomware less profitable, even though that doesn't help the copy of you in this timeline)?
It's a tough call! If your business's files are sufficiently important, then I can definitely see why you'd want to pay! But if someone were to try to portray the act of paying as pro-social, that would be pretty weird. If your Society knew how, law-abiding citizens would prefer to coordinate not to pay attackers, which is why the U.S. Treasury Department is cracking down on facilitating ransomware payments. But if that's not an option ...
our behavior [...] punishment against us [...] some other entity that we shouldn't care much about
If coordinating to resist extortion isn't an option, that makes me very interested in trying t...
I'm fairly aware of Murray's public image, but wanted to go a little deeper before replying.
Here's a review from the Washington Post this year, of Murray's latest book. Note that, while critical of his book, it does not call him a racist. Perhaps its strongest critical language is the closing sentence:
He writes as if his conclusions are just a product of cold calculus and doesn’t pause long enough to consider that perhaps it’s the assumptions in his theorem that are antithetical to the soul of America.
It actually more portrays him as out of touch with the rise of the far right than in lockstep with it. The article does not call him a racist, predict his book will cause harm, or suggest that readers avoid it. This suggests to me that there is still room for Murray's output to be considered by a major, relatively liberal news media outlet.
The Standard-Examiner published a positive review of the same book. They are a newspaper with a circulation of about 30,000, based out of Ogden, UT.
Looking over other the couple dozen news articles that popped up containing "Charles Murray" and "The Bell Curve" from 2021, I see several that mention protests against him, or arguments over TBC, mentio...
We've have a norm against discussing politics since before LessWrong 2.0, which doesn't seem to have had any noticeable negative effects on our ability to discuss other topics.
I'm not sure whether that's true, but separately, the norm against politics has definitely impact our ability to discuss politics. Perhaps that's a necessary sacrifice, but it's a sacrifice. In this particular case, both the object level (why is our society the way it is) and the meta-level (what are the actual views in this piece that got severe backlash) are relevant to our modeling of the world and I think it'd be a loss to not have this piece.
I do think that if we order all posts by where they appear on this spectrum, I would put this farther to the right than any other post I remember, so we genuniely seem to differ in our judgment here.
I'm not sure where this post would fall in my ranking (along the dimension you're pointing at). It's possible I agree with you that it's at the extreme end–but there has to be a post at the extreme end. The posts that are imo (or other moderator's opinions) over the line are ones you wouldn't see.
...I echo anon03 in that the title is extremely provocative, but minus the clai
Just a short note that the title seems like the correct one so that it's searchable by the name of the book slash author. Relatedly, all book reviews on LW are called "Book Review: <Book Name>", this one didn't stand out as any different to me (except it adds the author's name, which seems pretty within reasonable bounds to me).
I'll bite, but I can't promise to engage in a lot of back-and-forth.
- The site is discussed somewhere, someone claims that it's a home for racism and points to this post as evidence. Someone else who would have otherwise become a valuable contributor reads it and decides not to check it out
- A woke and EA-aligned person gets wind of it and henceforth thinks all x-risk related causes are unworthy of support
Let's generalize. A given post on LW's frontpage may heighten or diminish its visibility and appeal to potential newcomers, or the visibility/appeal of associated causes like X-risk. You've offered one reason why this post might heighten its visibility while diminishing its appeal.
Here's an alternative scenario, in which this post heightens rather than diminishes the appeal of LW. Perhaps a post about the Bell Curve will strike somebody as a sign that this website welcomes free and open discourse, even on controversial topics, as long as it's done thoughtfully. This might heighten, rather than diminish, LW's appeal, for a person such as this. Indeed, hosting posts on potentially controversial topics might select for people like this, and that might not only grow the website, but reinf...
I believe that LW must be have a readership two orders of magnitude lower than SSC/ACX (in the thousands, or even just the hundreds, for LW, in the hundreds of thousands for SSC/ACX)
LW's readership is about the same order of magnitude as SSC. Depending on the mood of the HN and SEO gods.
Not that I don't believe you, but that's also really hard for me to wrap my head around. Can you put numbers on that claim? I'm not sure if ACX has a much smaller readership than I'd imagined, or if LW has a much bigger one, but either way I'd like to know!
https://www.similarweb.com/website/astralcodexten.substack.com/?competitors=lesswrong.com Currently shows ACX at something like 1.7x of LessWrong. At some points in the past LessWrong was slightly ahead.
LessWrong is a pretty big website. Here is a random snapshot of top-viewed pages from the last month from Google Analytics:
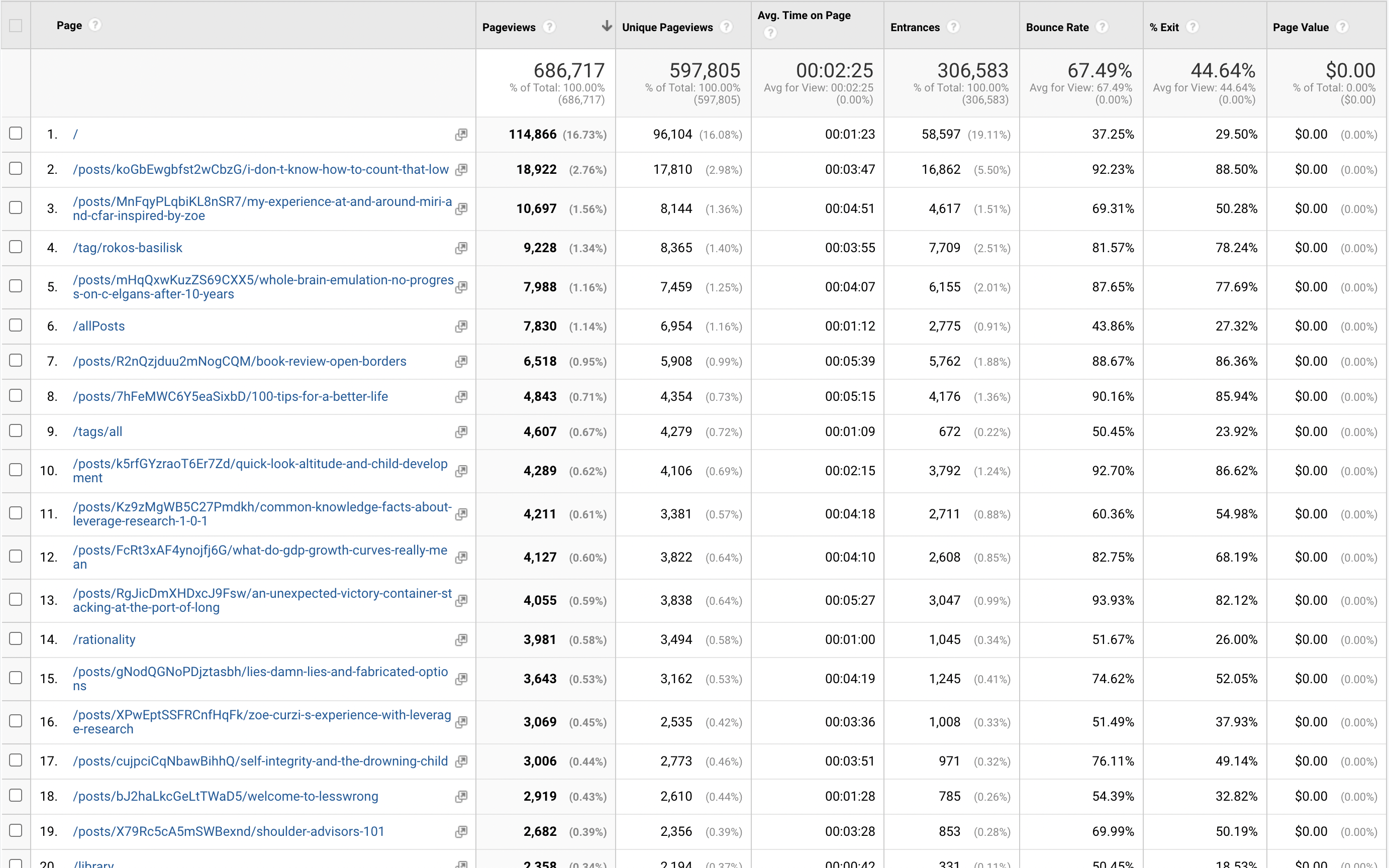
As you can see from the distribution, it's a long tail of many pages getting a few hundred pageviews each month, which adds up a lot.
Note that LW gets 1-2 OOM fewer comments on the average post, but not in total. I reckon monthly comments is same OOM. And if you add up total word count on each site I suspect LW is 1 OOM bigger each month. ACX is more focused and the discussion is more focused, LW is a much broader space with lots of smaller convos.
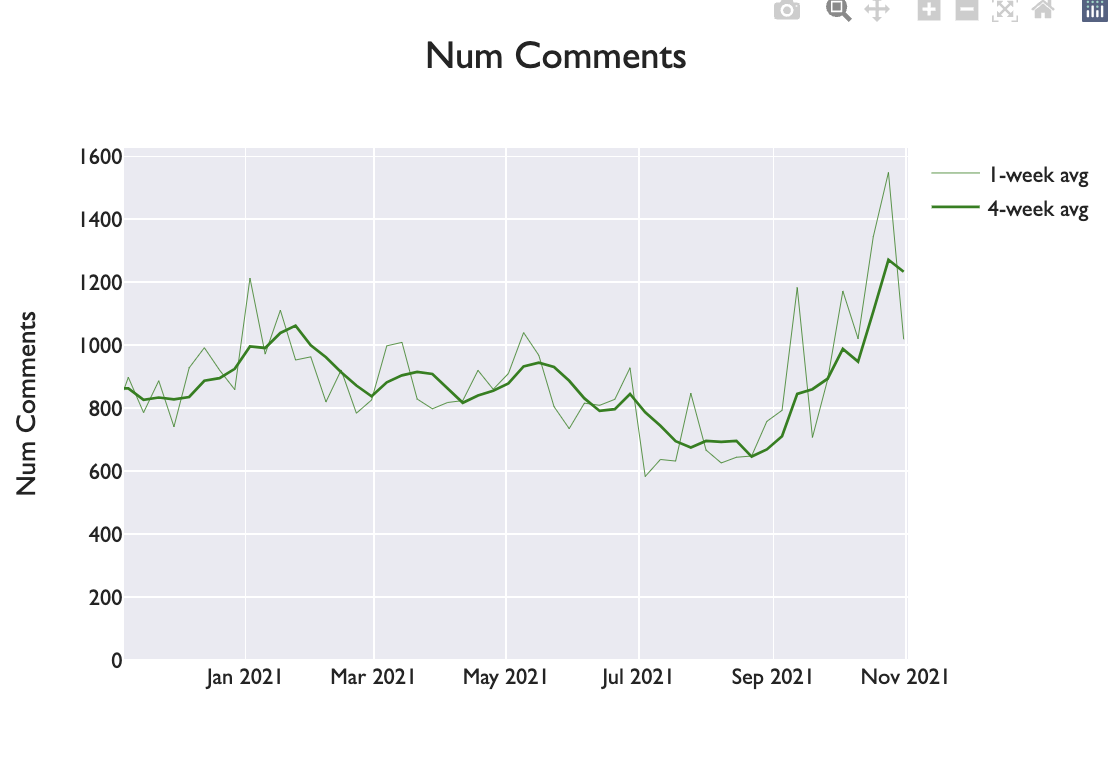
This is weekly comments for LessWrong over the last year. Last we counted, something like 300 on a SSC post? So if there are two SSC posts/week, LessWrong is coming out ahead.
Sam Harris has enormous reach, comparable to Scott’s. Also, podcasts have a different cultural significance than book reviews. Podcasts tend to come with an implicit sense of friendliness and inclusion extended toward the guest. Not so in a book review, which can be bluntly critical. So for the reasons I outlined above, I don’t think Harris’s experiences are a good reference class for what we should anticipate.
“Wokeism” is powerful, and I agree that this post elevated this site’s risk of being attacked or condemned either by the right or the left. I also agree that some people have been turned off by the views on racism or sexism they’ve been exposed to on by some posters on this site.
I also think that negativity tends to be more salient than approval. If lsusr’s post costs us one long-term reader and gains us two, I expect the one user who exits over it to complain and point to this post, making the reason for their dissatisfaction clear. By contrast, I don’t anticipate the newcomers to make a fanfare, or to even see lsusr’s post as a key reason they stick around. Instead, they’ll find themselves enjoying a site culture and abundance of posts that they find generally appealing. So...
After reading this, I realize that I've done an extremely poor job communicating with everything I've commented on this post, so let me just try to start over.
I think what I'm really afraid of is a sequence of events that goes something like this:
- Every couple of months, someone on LW makes a post like the above
- In some (most?) cases, someone is going to speak up against this (in this case, we had two), there will be some discussion, but the majority will come down on the side that censorship is bad and there's no need to take drastic action
- The result is that we never establish any kind of norm nor otherwise prepare for political backlash
- In ten or twenty or forty years from now, in a way that's impossible to predict because any specific scenario is extremely unlikely, the position to be worried about AGI will get coupled to being anti social justice in the public discourse, as a result it will massively lose status and the big labs react by taking safety far less seriously and maybe we have fewer people writing papers on alignment
- At that point it will be obvious to everyone that not having done anything to prevent this was a catastrophic error
After the discussion on the datin...
I will say that although I disagree with your opinion re: censoring this post and general risk assessment related to this issue, I don't think you've expressed yourself particularly poorly. I also acknowledge that it's hard to manage feelings of anxiety that come up in conversations with an element of conflict, in a community you care about, in regards to an issue that is important to the world. So go easier on yourself, if that helps! I too get anxious when I get downvoted, or when somebody disagrees with me, even though I'm on LW to learn, and being disagreed with and turning out to be wrong is part of that learning process.
It sounds like a broader perspective of yours is that there's a strategy for growing the AGI safety community that involves keeping it on the good side of whatever political faction is in power. You think that we should do pretty much whatever it takes to make AGI safety research a success, and that this strategy of avoiding any potentially negative associations is important enough for achieving that outcome that we should take deliberate steps to safeguard its perception in this way. As a far-downstream consequence, we should censor posts like this, out of a ...
I don't think anything of what I'm saying involves judging arguments based on their impact on the world.
What I mean here is that you, like most advocates of a marginal increase in censorship, justify this stance on the basis that the censored material will cause some people, perhaps its readers or its critics, to take an action with an undesirable consequence. Examples from the past have included suicidal behavior, sexual promiscuity, political revolution, or hate crimes.
To this list, you have appended "elevating X-risk." This is what I mean by "impact on the world."
Usually, advocates of marginal increases in censorship are afraid of the content of the published documents. In this case, you're afraid not of what the document says on the object level, but of how the publication of that document will be perceived symbolically.
An advocate of censorship might point out that we can potentially achieve significant gains on goals with widespread support (in our society, stopping hate crimes might be an example), with only modest censorship. For example, we might not ban sales of a certain book. We just make it library policy not to purchase them. Or we restrict purchase to a certain age g...
Anecdotal, but about a year ago I committed to the rationalist community for exactly the reasons described. I feel more accepted in rationalist spaces than trans spaces, even though rationalists semi-frequently argue against the standard woke line and trans spaces try to be explicitly welcoming.
I like the norm of “If you’re saying something that lots of people will probably (mis)interpret as being hurtful and insulting, see if you can come up with a better way to say the same thing, such that you’re doing that.” This is not a norm of censorship nor self-censorship, it’s a norm of clear communication and of kindness.
I think that this is completely wrong. Such a norm is definitely a norm of (self-)censorship—as has been discussed on Less Wrong already.
It is plainly obvious to any even remotely reasonable person that the OP is not intended as any insult to anyone, but simply as a book review / summary, just like it says. Catering, in any way whatsoever, to anyone who finds the current post “hurtful and insulting”, is an absolutely terrible idea. Doing such a thing cannot do anything but corrode Less Wrong’s epistemic standards.
Suppose that Person A finds Statement X demeaning, and you believe that X is not in fact demeaning to A, but rather A was misunderstanding X, or trusting bad secondary sources on X, or whatever.
What do you do?
APPROACH 1: You say X all the time, loudly, while you and your friends high-five each other and congratulate yourselves for sticking it to the woke snowflakes.
APPROACH 2: You try sincerely to help A understand that X is not in fact demeaning to A. That involves understanding where A is coming from, meeting A where A is currently at, defusing tension, gently explaining why you believe A is mistaken, etc. And doing all that before you loudly proclaim X.
I strongly endorse Approach 2 over 1. I think Approach 2 is more in keeping with what makes this community awesome, and Approach 2 is the right way to bring exactly the right kind of people into our community, and Approach 2 is the better way to actually "win", i.e. get lots of people to understand that X is not demeaning, and Approach 2 is obviously what community leaders like Scott Alexander would do (as for Eliezer, um, I dunno, my model of him would strongly endorse approach 2 in principle, but also sometimes he likes to troll...
Imagine that Person A believes that Charles Murray is a notorious racist, and TBC is a book that famously and successfully advocated for institutional racism via lies and deceptions. You don’t have to actually believe this—I don’t—I am merely asking you to imagine that Person A believes that.
If Person A believes this without ever having either (a) read The Bell Curve or (b) read a neutral, careful review/summary of The Bell Curve, then A is not a reasonable person.
All sorts of unreasonable people have all sorts of unreasonable and false beliefs. Should we cater to them all?
No. Of course we should not.
Now look at the OP through A’s eyes. Right from the title, it’s clear that OP is treating TBC as a perfectly reasonable respectable book by a perfectly reasonable respectable person.
The title, as I said before, is neutrally descriptive. Anyone who takes it as an endorsement is, once again… unreasonable.
Now A starts scanning the article, looking for any serious complaint about this book, this book which by the way personally caused me to suffer by successfully advocating for racism
Sorry, what? A book which you (the hypothetical Person A) have never read (and in fact have only...
Sorry, what? A book which you (the hypothetical Person A) have never read (and in fact have only the vaguest notion of the contents of) has personally caused you to suffer? And by successfully (!!) “advocating for racism”, at that? This is… well, “quite a leap” seems like an understatement; perhaps the appropriate metaphor would have to involve some sort of Olympic pole-vaulting event. This entire (supposed) perspective is absurd from any sane person’s perspective.
I have a sincere belief that The Protocols Of The Elders Of Zion directly contributed to the torture and death of some of my ancestors. I hold this belief despite having never read this book, and having only the vaguest notion of the contents of this book, and having never sought out sources that describe this book from a "neutral" point of view.
Do you view those facts as evidence that I'm an unreasonable person?
Further, if I saw a post about The Protocols Of The Elders Of Zion that conspicuously failed to mention anything about people being oppressed as a result of the book, or a post that buried said discussion until after 28 paragraphs of calm open-minded analysis, well, I think I wouldn't read through the whole p...
Your analogy breaks down because the Bell Curve is extremely reasonable, not some forged junk like "The Protocols Of The Elders Of Zion".
If a book mentioned here mentioned evolution and that offended some traditional religious people, would we need to give a disclaimer and potentially leave it off the site? What if some conservative religious people believe belief in evolution directly harms them? They would be regarded as insane, and so are people offended by TBC.
That's all this is by the way, left-wing evolution denial. How likely is it that people separated for tens of thousands of years with different founder populations will have equal levels of cognitive ability. It's impossible.
Hmm, I think you didn't get what I was saying. A book review of "Protocols of the Elders of Zion" is great, I'm all for it. A book review of "Protocols of the Elders of Zion" which treats it as a perfectly lovely normal book and doesn't say anything about the book being a forgery until you get 28 paragraphs into the review and even then it's barely mentioned is the thing that I would find extremely problematic. Wouldn't you? Wouldn't that seem like kind of a glaring omission? Wouldn't that raise some questions about the author's beliefs and motives in writing the review?
Do you view those facts as evidence that I’m an unreasonable person?
Yeah.
Do you ever, in your life, think that things are true without checking? Do you think that the radius of earth is 6380 km? (Did you check? Did you look for skeptical sources?) Do you think that lobsters are more closely related to shrimp than to silverfish? (Did you check? Did you look for skeptical sources?) Do you think that it's dangerous to eat an entire bottle of medicine at once? (Did you check? Did you look for skeptical sources?)
I think you're holding people up to an unreasonable standard here. You can't do anything in life without havin...
Hmm, I think you didn’t get what I was saying. A book review of “Protocols of the Elders of Zion” is great, I’m all for it. A book review of “Protocols of the Elders of Zion” which treats it as a perfectly lovely normal book and doesn’t say anything about the book being a forgery until you get 28 paragraphs into the review and even then it’s barely mentioned is the thing that I would find extremely problematic. Wouldn’t you? Wouldn’t that seem like kind of a glaring omission? Wouldn’t that raise some questions about the author’s beliefs and motives in writing the review?
I agree completely.
But note that here we are talking about the book’s provenance / authorship / otherwise “metadata”—and certainly not about the book’s impact, effects of its publication, etc. The latter sort of thing may properly be discussed in a “discussion section” subsequent to the main body of the review, or it may simply be left up to a Wikipedia link. I would certainly not require that it preface the book review, before I found that review “acceptable”, or forebore to question the author’s motives, or what have you.
And it would be quite unreasonable to suggest that a post titled “Book Review: The Protocol...
Approach 2 assumes that A is (a) a reasonable person and (b) coming into the situation with good faith. Usually, neither is true.
What is more, your list of two approaches is a very obvious false dichotomy, crafted in such a way as to mock the people you’re disagreeing with. Instead of either the strawman Approach 1 or the unacceptable Approach 2, I endorse the following:
APPROACH 3: Ignore the fact that A (supposedly) finds X “demeaning”. Say (or don’t say) X whenever the situation calls for it. Behave in all ways as if A’s opinion is completely irrelevant.
(Note, by the way, that Approach 2 absolutely does constitute (self-)censorship, as anything that imposes costs on a certain sort of speech—such as, for instance, requiring elaborate genuflection to supposedly “offended” parties, prior to speaking—will serve to discourage that form of speech. Of course, I suspect that this is precisely the goal—and it is also precisely why I reject your suggestion wholeheartedly. Do not feed utility monsters.)
As I mentioned elsethread, if I'd written the book review I would have done what you describe. But I didn't and probably never would have written it out of timidness, and that makes me reluctant to tell someone less timid who did something valuable that they did it wrong.
Strong-downvoted. I want lesswrong to be a peaceful place where we can have polite boring truth-seeking arguments without incurring reputational risk / guilt-by-association. I understand the benefit of having polite boring truth-seeking arguments about racism-adjacent topics that take sides in an incredibly incendiary culture war. However, there is also a cost—namely, there's a public good called "right now there is minimal reputational risk of being publicly IRL known as a lesswrong participant", and each time there's a post about racism-adjacent topics t...
I agree the post didn't address Murray's points that critically or look deeply into the long list of critiques of the book, but it's a useful summary of the main points (with some criticism here and there), which I think was the point.
I'm not sure how most of these options would ensure the benefit of summarizing without the cost of reputational risk: (1) This one might, until the connections are easily followed by, say, the NYT or any random internet sleuth; (2) Maybe the title has been edited (?), but I'm not seeing a provocative title or framing, most of it isn't even about race; (3) The example here isn't even about race and is obviously not about moral worth though the general point is good from an editing standpoint; (4) Certainly this would enhance the contribution (I wanted some of this myself), but particularly when it comes to The Bell Curve, people have this misconception that it's just a racist screed, so a summary from someone who actually read the book is helpful to start. Maybe a summary just isn't up to the contribution level of a LW post and one should hit a higher bar - but that's a norm that has yet to be established IMHO.
Intelligence and race are both uncomfortable topics, and mixing them together is even more uncomfortable. If LW wants a norm of not discussing particular uncomfortable topics, then okay! But at least let it be through topic-screening rather than overblowing what is actually being said in a post.
Could someone please steelman the position of people who disagree strongly with this book? Which parts of the book are considered factually or logically incorrect, which parts do people object to so strongly on moral grounds, etc.?
Please be alright, it's a horrible thing to be robbed. I don't think I can help from here, but still.
Possible typo: "Being smart causes work-inhibiting disability." given that the chart you then show says the opposite.
Archived.
https://web.archive.org/web/20211103174524/https://www.lesswrong.com/posts/vvc2MiZvWgMFaSbhx/book-review-the-bell-curve-by-charles-murray
Factor analysis is a mathematical method of inferring simple correlations between observations. It's the foundation of the Big Five personality traits. It's also behind how we define intelligence.
A person's ability to perform one cognitive task is positively correlated with basically every other cognitive task. If you collect a variety of cognitive measures you can use linear algebra to extract a single measure which we call g. Intelligence quotient (IQ) is a test specifically designed to measure g. IQ isn't a perfect measure of g but it's convenient and robust.
Charles Murray doesn't bother proving the above points. These facts are well established among scientists. Instead, The Bell Curve: Intelligence and Class Structire in American Life is about what g means to American society.
Stratification
Educational Stratification
Smarter people have always had an advantage. The people who go to college have always been smarter than average. The correlation between college and intelligence increased after WWII. Charles Murray argues that the competitive advantage of intelligence is magnified in a technological society. I agree that this has been the case so far and that the trend has continued between 1994 when Murray published his book and 2021 when I am writing this review.
SAT scores can be mapped to IQ. The entering class of Harvard in 1926 had a mean IQ of about 117. IQ is defined to have an average of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Harvard in 1926 thus hovered around the 88th percentile of the nation's youths. Other colleges got similar scores. The average Pennsylvania college was lower with an IQ of 107 (68th percentile). Elite Pennsylvania colleges had students between the 75th and 90th percentiles.
By 1964, the average student of a Pennsylvania college had an IQ in the 89th percentile. Elite colleges' average freshmen were in the 99th percentile.
Charles Murray uses a measure called median overlap to quantify social stratification. Median overlap indicates what proportion of IQ scores the lower-scoring group matched or exceeded the median score in the higher-scoring group. Two identical groups would have a median overlap of 50%.
College graduates are not representative of the population. If most of your social circle is (or will be) a college graduate then your social circle is smarter than the population mean.
Occupational Stratification
You can arrange jobs by their relative status. Job status tends to run in families. This could be because of social forces or it could be because of heritable g. We can test which hypothesis is true via an adoptive twin study. A study in Denmark tracked several hundred men and women adopted before they were one year old. "In adulthood, they were compared with both their biological siblings and their adoptive siblings, the idea being to see whether common genes or common home life determined where they landed on the occupational ladder. The biologically related siblings resembled each other in job status, even though they grew up in different homes. And among them, the full siblings had more similar job status than the half siblings. Meanwhile, adoptive siblings were not significantly correlated with each other in job status."
High-status jobs have become much more cognitively demanding over the last hundred years. Charles Murray uses a bunch of data to prove this. I'll skip over his data because the claim it's so obviously to someone living in the Internet age. Even being an marketer is complicated these days.
Credentialism is a real thing. Could it be that IQ causes education which causes high status jobs but cognitive ability doesn't actually increase job performance? Or does sheer intellectual horsepower have market value? We have data to answer this question.
IQ tests frequently measure one's ability to solve abstract puzzles. Programming interview algorithm puzzles are tests of a person's abstract problem-solving ability. I wonder how much of Google's algorithm interview tests predictive power comes from g factor. Some of it must. The question is: How much? If the answer is "a lot" then these tests could be a de facto workaround for the 1971 Supreme Court case Griggs v. Duke Power Co. which found that IQ-based employment constituted employment discrimination under disparate impact theory.
The best experiments compel lots of people people to do things. The US military compels a lots of people to do things. Thus, some of our best data on g's relationship to job performance comes from the military.
"[T]he explanatory power of g was almost thirty times greater than of all other cognitive factors in ASVAB combined." In addition, the importance of g was stronger for more complicated tasks. Other military studies find similar results to this one.
There's no reason to believe civilian jobs are any less dependent on g than military jobs. For cognitively-demanding jobs like law, neurology and research in the hard sciences, we should expect the percentage of training success explained by g to be well over 70%. Similar results appear for civilian jobs.
If we measure civilian job performance instead of military training success we get a smaller (but still large) impact of g. Note that the measures below probably contain significant overlap. Part of college grades' predictive power comes from them being an imperfect measure of g.
Charles Murray's data shows that a secretary or a dentist who is one standard deviation better than average is worth a 40% premium in salary. Such jobs undersell the impact of worker variation among job performers. Jobs with leverage have a disproportionate impact on society. Anyone who has worked in a highly-technical field with leverage (like software developers, scientists or business executives) knows that someone one standard deviation above average is worth much more than 40% more.
As technology advances, the number of highly-technical jobs with leverage increases. This drives up the value of g which increases income inequality.
Social Partitioning
The cognitive elite usually partition ourselves off into specialized neighborhoods. For example, I live in Seattle. Seattle is one of the most software-heavy cities in the world. Seattle contains headquarters of Microsoft and Amazon are here. You can barely throw a router without hitting a programmer. You'd expect highschools to be full of technical volunteers. But that's only in the rich neighborhoods. I, weirdly, live in a poor, dangerous[1] neighborhood where I volunteer as a coach for the local high school's robotics club. If I wasn't around there would be no engineers teaching or coaching at the highschool. None of my friends live here. They all live in the rich, safe neighborhoods.
Heritability of Intelligence
The heritability of intelligence combines with cognitive stratification to increase IQ variance. The average husband-wife IQ correlation is between .2 and .6. Whatever the number used to be, I expect it has increased in the 27 years since The Bell Curve was published. Technically-speaking, elite graduates have always married each other. However, the concentration of cognitive ability among elites increases the genetic impact of this phenomenon.
Negative Effects of Low Intelligence
All the graphs in this section control for race by including only white people.
Poverty
Is poverty caused by IQ or by one's parents' social class? What would you bet money that the answer is?
Parental social economic status matters but the impact is small compared to IQ.
The black lines intersect at an IQ of 130. I think that once you pass a high enough threshold of intelligence, school stops mattering because you can teach yourself things faster than schools can teach you. Credentials don't matter either because exceptional people are wasted in cookie-cutter roles.
High School Graduation
There was no IQ gap between high school dropouts and graduates in the first half of the 20th century, before graduating high school became the norm. After high school became the norm, dropouts became low IQ.
In this case, IQ is even more predictive than parental social economic status. However, for temporary dropouts, social economic status matters a lot. (In terms of life outcomes, youths with a GED look more like dropouts than high school graduates.)
The image I (and Charles Murray) get is of dumb rich kids who get therapists, private tutors, special schools—the works. Highschool is easier to hack than college (and work, as we'll get to later). The following graph is, once again, white youths only.
Labor Force Participation
Being smart causes you to work more. Being born rich causes you to work less.
Being smart reduces the likelihood of a work-inhibiting disability.
Lower-intelligence jobs tend to involve physical objects which can injure you. However, this fails to account for the whole situation. "[G]iven that both men have blue-collar jobs, the man with an IQ of 85 has double the probability of a work disability of a man with an IQ of 115…the finding seems to be robust." It could be that dumb people are more likely to injure themselves or that they misrepresent their reasons not working or both.
Technically, unemployment is different from being out of the labor force. Unemployment also shows that being smart is negatively correlated with being unemployed in 1989.
Parental socioeconomic status had no measurable effect on unemployment. All that money spent on buying a high school diploma does not transfer to increased employment status. The following graph is of white men.
Family
Young white women with lower IQ are much more likely to give birth to an illegitimate baby in absolute terms and relative to legitimate births. How much more?
As usual, IQ outweighs parental socioeconomic status. The following graph is for white women.
Remember that IQ correlates with socioeconomic status. "High socioeconomic status offered weak protection against illegitimacy once IQ had been taken into account."
Welfare Dependency
Charles Murray gives a bunch of graphs and charts about how IQ affects welfare dependency. I bet you can guess what kind of a relationship they show.
Parenting
Surprisingly to me, the mother's age at birth of the child did not affect her changes of giving birth to a low-birth-weight baby. Poverty didn't matter either. I suspect this is because America has a calorie surplus. I predict poverty was a very important factor in extremely poor pre-industrial societies.
A mother's socioeconomic background does have a large effect (independent of the mother's IQ) of her child's chances of spending the first years of its life in poverty. This isn't to say IQ doesn't matter. It's just the first result in our entire analysis where IQ doesn't dominate all other factors.
Mother IQ does have a big impact on the quality of her childrens' home life.
The children of mothers with low IQs have worse temperaments (more difficulty and less friendliness), worse motor & social development and more behavior problems. (There's a bump in some worse outcomes for the smartest mothers, but this might just be an artifact of the small sample size.) The mother's socioeconomic background has a large effect on childrens' development problems, though not quite as high as the mother's IQ.
If you want smart kids then a smart mother is way more important than the mother's socioeconomic background. By now, this should come as no surprise.
Crime
High IQ correlates with not getting involved with the criminal justice system. Move along.
Ethnicity and Cognition
Different ethnic groups vary on cognitive ability.
"Do Asians Have Higher IQs than Whites? Probably yes, if Asian refers to the Japanese and Chinese (and perhaps also Koreans), whom we will refer here as East Asians." Definitely yes if "Asian" refers to Chinese-Americans. This can be entirely explained by US immigration policy. It is hard to get into the USA if you are an East Asian. The United States has discriminated against Asian immigrants for most of its history and continues to do so. The United States is a desirable place to life. If you're an Asian and you want to get into the US then it helps to be smart. If would be weird if Asian-Americans weren't smarter than other immigrants. ("Other immigrants" includes all non-Asian, non-Native Americans.) Since intelligence is significantly heritable and people tend to intermarry among our own ethnic groups (often because the alternative was illegal[2]), a founder effect can be expected to persist across the handful of generations the United States has existed for.
The Bell Curve is mostly about America. It's disconcerting to me when he suddenly compares American students to students from Japan and Hong Kong. When he says "black" he uses a sample of African-American (and not Africa-African) but when he says "Japanese" he uses a sample of Japan-Japanese (and not Japanese-American). When he says "Jews" he includes the whole global diaspora and not (I presume) Latino converts.
I think Charles Murray fails to realize that Asian-Americans are such a biased sample of Asians that the two must be separated when you're studying g. Fortunately, Asia-Asians are not a critical pillar of Murray's argument. Charles Murray tends to bucket Americans into black and white and somtimes Latino.
Black and White Americans
These differences are statistical. They apply to populations.
People frequently complain of IQ tests being biased. It is possible to determine whether a test is biased.
"If the SAT is biased against blacks, it will underpredict their college performance. If tests were biased in this way, blacks as a group would do better in college than the admissions office expected based on just their SATs." In either case "[a] test biased against blacks does not predict black performance in the real world in the same way that it predicts white performance in the real world. The evidence of bias is external in the sense that it shows up in differing validities for blacks and whites. External evidence of bias has been sought in hundreds of studies. It has been evaluated relative to performance in elementary school, in secondary school, in the university, in the armed forces, in unskilled and skilled jobs, in the professions. Overwhelmingly, the evidence is that the major standardized tests used to help make school and job decisions do not underpredict black performance, nor does the expert community find that other general or systematic difference in the predictive accuracy of tests for blacks and whites."
IQ tests often involve language. A smart Russia-Russian genius who does not speak English would fail an IQ test given in English. "For groups that have special language considerations—Latinos and American Indians, for example—some internal evidence of bias has been found, unless English is their native language." Native language is not an issue for African-Americans because African-Americans are native English speakers.
What about cultural knowledge? "The [black-white] difference is wider on items that appear to be culturally neutral than on items that appear to be culturally loaded. We italicise this point because it is both so well established empirically yet comes as such a surprise to most people who are new to this topic."
What about test-taking ability and motivation? We can test whether testing itself is behind a black-white difference by comparing standard IQ tests to tests of memorizing digits. Reciting digits backwards takes twice as much g as reciting them forward. This experiment controls for test-taking ability and motivation because the forward and backward recitations are given under identical conditions. The black-white difference is about twice as great concerning reciting digits backwards as it is concerning reciting digits forwards.
Reaction correlates strongly with g but movement time is less correlated. Whites consistently beat blacks on reaction time even tests though black movement time is faster than white movement time.
Any explanation for a the black-white IQ difference based on culture and society must explain the IQ difference, the number recitation difference, the reaction time difference, the movement time similarity and the difference in every cognitive measures of performance and achievement.
Lead in the water or epigenetic effects of slavery would constitute such an explanation. Such explanations would throw into doubt whether the difference is genetic but would also prove biological determinism.
What about socioeconomic status? The size of the black-white IQ gaps shrinks when socioeconomic status is controlled for. However, socioeconomic status is at least partially a result of cognitive ability. "In terms of the numbers, a reasonable rule of thumb is that controlling for socioeconomic status reduces the overall B/W difference by about third."
We can test for whether socioeconomic status causes the IQ difference by comparing blacks and whites of equal socioeconomic status. If the black-white IQ difference was caused by socioeconomic status then blacks and whites of equal socioeconomic status would have similar IQs. This is not what we observe.
It might be that the black-white difference comes from a mix of socioeconomic status plus systemic racism.
Africa
Charles Murray's analysis of Africa-Africans bothers me for the same reason his analysis of Asians bothers me. In this case, he assumes African-Americans are representative of Africa-Africans. For instance, he discusses how difficult it is "to assemble data on the average African black" even though African-Americans are mostly from West Africa. Given pre-historical human migration patterns, it is my understanding that West Africans are more genetically distant from East Africans than White people are from Asians. If I am right about Africa-African diversity then Africa-Africans are too broad of a reference class. He should be comparing African-Americans to West Africans[3].
Charles Murray believes scholars are reluctant to discuss Africa-African IQ scores because they are so low. I think he means to imply that African-African and African-American IQs are genetically connected. I think such a juxtaposition undersells the Flynn Effect. Industrialization improves the kind of abstract reasoning measured by IQ tests. Fluid and crystallized intelligence have both increased in the rich world in the decades following WWII. The increase happened too fast for it to be because of evolution. It might be due to better health or it could be because our environment is more conducive to abstract thought. I suspect the Flynn Effect comes from a mix of both. The United States and Africa are on opposite ends of the prosperity spectrum. Charles Murray is careful to write "ethnicity" instead of "race", but his classification system is closer to how I think about race than how I think about ethnicity. African-Americans and Africa-Africans are of the same race but different ethnicities.
I disagree with Charles Murray's logic here. Suppose (in contradiction to first-order genetic pre-history) that Africa-Africans and the African diaspora were genetically homogeneous. A difference in IQ between African-Americans and Africa-Africans would imply that which society you live in substantially influences IQ. If America is segregated in such a way that kept African-Americans living in awful conditions then we would expect African-Americans' IQs to be depressed. Jim Crow laws were enforced until 1965. Martin Luther King Jr. was shot in 1968, a mere 26 years before the publication of The Bell Curve. Blacks and whites continue to be de facto racially segregated today in 2021. Even if racism ended in 1965 (it didn't), 29 years is not enough time to complete erase the damage caused by centuries of slavery and Jim Crow.
Charles Murray does acknowledge the possible effect of systemic racism. "The legacy of historic racism may still be taking its toll on cognitive development, but we must allow the possibility that it has lessened, at least for new generations. This too might account for some narrowing of the black-white gap."
Black-White Trends
The black-white gap narrowed in the years leading up to the publication of The Bell Curve. This is exactly what we would expect to observe if IQ differences are caused by social conditions because racism has been decreasing over the decades.
Charles Murray acknowledges that rising standards of living increase the intelligence of the economically disadvantaged because improved nutrition, shelter and health care directly removes impediments to brain development. The biggest increase in black scores happened at the low end of the range. This is evidence that improved living conditions of life improved IQ because the lowest hanging fruit hangs from the bottom end of the socioeconomic ladder.
How much is genetic?
Just because something is heritable does not mean the observed differences are genetic in origin. "This point is so basic, and so commonly misunderstood, that it deserves emphasis: That a trait is genetically transmitted in individuals does not mean that group differences in that trait are also genetic in origin." For example, getting skinny early can be caused by genetics or it can be caused by liposuction. The fact that one population is fat and another population is skinny does not mean that the difference was caused by genetics. It could just be that one group has better access to liposuction.
As demonstrated earlier, socioeconomic factors do not influence IQ much. For the black-white difference to be explained by social factors, those factors would have to exclude socioeconomic status.
One plausible reason is that Chinese-Americans and Jews value academic success stronger than whites and blacks. African-Americans' African culture was systematically destroyed by slavery. They never got the academic cultural package. We could test the cultural values hypothesis by examining at what happens when Chinese or Jewish kids are raised by white families and vice versa. The Bell Curve doesn't have this particular data but it does have white-black data. An examination of 100 adopted children of black, white and mixed racial ancestery found that "[t]he bottom line is that the gap between the adopted children with two black parents and the adopted children with two white parents was seventeen points, in line with the B/W difference customarily observed. Whatever the environmental impact may have been, it cannot have been large." This is evidence against the cultural transmission hypothesis—at least when comparing blacks and whites. Several other studies "tipped toward some sort of mixed gene-environment explanation of the B/W difference without saying how much of the difference is genetic and how much environmental…. It seems highly likely to us that both genes and the environment have something to do with racial differences. What might the mix be? We are resolutely agnostic on that issue; as far as we can determine, the evidence does not yet justify an estimate…. In any case, you are not going to learn tomorrow that all the cognitive differences between races are 100 percent genetic in origin, because the scientific state of knowledge, unfinished as it is, already gives ample evidence that environment is part of the story."
The study of Korean infants seems like the right way to answer this question. The only issue is the small sample size.
What's especially interesting to me, personally, is that "East Asians living overseas score about the same or slightly lower than whites on verbal IQ and substantially higher on visuospatial IQ." This suggests to me that the stereotype of white managers supervising Asian engineers might reflect an actual difference in abilities. (If anyone has updated evidence which contradicts this, please put it in the comments.)
"This finding has an echo in the United States, where Asian-American students abound in engineering, in medical schools, and in graduate programs in the sciences, but are scarce in laws schools and graduate programs in the humanities and the social sciences." I agree that unfamiliarity with the English and American culture is not a plausible explanation for relatively subpar Asian-American linguistic performance. Asian-Americans born in the United States are fluent English speakers. However, I offer an alternative explanation. It could be that engineering, medicine and the sciences are simply more meritocratic than law, the humanities and the social sciences.
Interestingly, "American Indians and Inuit similarly score higher visuospatial than verbally; their ancestors migrated to the Americas from East Asia hundreds of centuries ago. The verbal-visuospatial discrepancy goes deeper than linguistic background." This surprised me since the Inuit are descended form the Aleut who migrated to America around 10,000 years ago—well before East Asian civilization. It's not obvious to me what environmental pressures would encourage higher visuospatial ability for Arctic Native Americans compared to Europeans.
Charles Murray dismisses the hypothesis that East Asian culture improves East Asians' visuospatial abilities.
I don't know what's going on with the Native Americans or exactly what "other Asian countries" includes (I'm betting it doesn't include Turks) but people from East Asia and the East Asian disapora have cultures that consistently value book learning. Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan and mainland China eat similar foods, write in similar ways, (except, perhaps, for Korea) are all cultural descendants of the Tang Dynasty.
If Native Americans have high IQ and high IQ improves life outcomes then why aren't Native Americans overrepresented in the tech sector? I was so suspicious of the Native Americans connection that I looked up the their IQ test scores. According to this website, Native American IQ is below average for the US and Canada. Native Americans seem to me like the odd ones out of this group. Sure, they might have relatively high visualspatial abilities compared to linguistic abilities. But Native American IQs are below East Asians'. I think Charles Murray is once again using too big of a bucket. East Asians and Native Americans should not be lumped together.
I think the common history of East Asians and Native Americans can (in this context[4]) be totally dismissed as irrelevant. Just look at alcohol tolerance. Native Americans were decimated when Europeans introduced alcohol. Meanwhile, East Asians have been drinking alcohol long enough to evolve the Asian flush. These populations have been separate for so long that one of them adapted to civilization in a way the other one didn't. Charles Murray proved that high visuospatial abilities help people rise to the top of a technically-advanced civilization. It would not surprise me one group that has competed against itself inside of the world's most technologically-advanced civilization for hundreds of generations had a higher visuospatial ability than another group which hasn't.
Race and Employment
Lots of (but not all) racial differences in life outcomes can be explained by controlling for IQ.
Projecting Demography
The higher the education, the fewer the babies.
Different immigrant populations have different IQs. Richard Lynn assigned "means of 105 to East Asians, 91 to Pacific populations, 84 to blacks, and 100 to whites. We assign 91 to Latinos. We know of no data for Middle East or South Asian populations that permit even a rough estimate." I like how the data here breaks Asians down into smaller groups. The average "works out to about 95" seems like a bad omeb but immigrants tend to come from worse places than the United States. I expect the Flynn effect will bring their descendents' average up.
While this makes sense on paper, we need to acknowledge a technical point about statistics. The Bell Curve is named after the Gaussian distribution. IQ is a Gaussian distribution. But that doesn't necessarily reflect a natural phemonenon. IQ tests are mapped to a Gaussian distribution by fiat. Charles Murray never proved that IQ is actually a Gaussian distribution. Many real-world phenomena are long-tailed. (Though biological phenomena like height are often Gaussian.) It is a perfectly reasonable prior that small changes to the mean could result in large effects at the tails. Ashkenazi Jewish history small changes to the mean do cause a massive impact on the tails. But I don't think the evidence presented in The Bell Curve is adequate to prove that g is Gaussian distributed.
Raising Cognitive Ability
If better measures of g have higher heritability that's a sign that it's the worse measures of g are easier to hack. If the heritability of IQ goes up as one ages that suggests youth interventions are just gaming the metrics—especially when youth interventions frequently produce only short-term increases in measured IQ.
Once a society has provided basic schooling and eliminated the obvious things like malnutrition and lead in the water, the best way to increase g will be eugenics. (I am bearish on AI parenting.) I am not advocating a return to the unscientific policies of the 20th century. Forcibly imposing eugenic policies is horrific and counterproductive. Rather, I predict that once good genetic editing technology is available, parents will voluntarily choose the best genes for their children. There will[5] come a day when not giving your kids the best genes will be seen by civilized people as backwards and reactionary. The shift in societal ethics will happen no later than a two generations (forty years) after the genetic editing of human zygotes becomes safe and affordable.
Besides cherry-pick our descendants' genotypes, is there anything else we can do? Improved nutrition definitely increases cognitive ability, but there is diminishing returns. Once you have adequate nutrition, getting more adequate nutrition doesn't do anything.
Having school (verses no school) does raise IQ. Thus, "some of the Flynn effect around the world is explained by the upward equalization of schooling, but a by-product is that schooling in and of itself no longer predicts adult intelligence as strongly…. The more uniform a country's schooling is, the more correlated the adult IQ is with childhood IQ." Increasing access to schooling increases the strength of natural differences on IQ because when you eliminate societally-imposed inequality all that's left is natural variation.
A whole bunch of programs purport to increase IQ but none of them show a significant long-term effect after many years. It seems to me like they're just gaming the short-term metrics. "An inexpensive, reliable method of raising IQ is not available."
Affirmative Action
College Affirmative Action
I'm not going to dive deep into Charles Murrays thoughts on affirmative action because they're incontrovertible. Affirmative action in college admissions prioritizes affluent blacks over disadvantaged whites. It's also anti-Asian.
Racist admissions harm smart blacks and Latinos.
Workplace Affirmative Action
Conclusion
Charles Murray ends with a chapter on where we're going, which he followed it up later with an entire book on class stratification among white Americans.
I was robbed at gunpoint last weekend. ↩︎
Interracial marriage was illegal in nearly every state before 1888. It remained illegal in 15 states all the way until 1967 when the laws were overturned by the Supreme Court ruling Loving v. Virginia. ↩︎
Unless Charles Murray believes that forces outlined in Jared Diamond's Guns, Germs and Steel (which, ironically, was written in opposition to race-based heritable theories of achievement differences) caused Eurasians to evolve higher g than their African forbears. While writing this footnote, I realized that the hypothesis is worth considering. Rice-based peoples evolved alcohol intolerance. Indian, Iraqi, Chinese and Japanese men evolved small penises. Software advances faster than hardware. It would be weird if civilization didn't cause cognitive adaptations too. I want to predict that cognitive adaptations to happen faster than physiological adaptations but I don't know how they can be compared. ↩︎
In Jared Diamond's Guns, Germs, and Steel context, Native Americans' sister relationship to East Asians does matter. ↩︎
As usual, this prediction is conditional on neither the singularity nor a civilizational collapse occurring. ↩︎